Suicide prevention for older adults has become a critical focus as this demographic faces alarming rates of self-harm, particularly among those aged 75 and over. Despite the increased vulnerability to mental health issues in seniors, the resources available for elderly suicide prevention remain woefully inadequate. Recent studies underscore the urgent need for targeted initiatives that address the unique challenges faced by this group, including social isolation and loneliness, which are significant contributors to the rising suicide rates in elderly populations. Geriatric psychiatry experts emphasize that a lack of accessible resources, coupled with limited online support, exacerbates the situation. As we strive for effective mental health solutions, it is essential to enhance awareness and accessibility of resources for elderly suicide prevention to safeguard our seniors’ well-being.
The challenge of preventing self-harm among the aging population highlights an urgent need for interventions tailored to their specific circumstances. As older individuals increasingly turn to the internet for information about mental health, the gap in available support is more pronounced than ever. Initiatives focusing on the high suicide rates among seniors not only aim to provide immediate resources but also to cultivate a better understanding of the factors affecting their mental health. By engaging with geriatric mental health professionals, advocates can help develop effective strategies and online resources for seniors that speak to their needs. As we broaden our conversation around suicide prevention in later life, it becomes crucial to address and adapt our approaches to this vulnerable group.
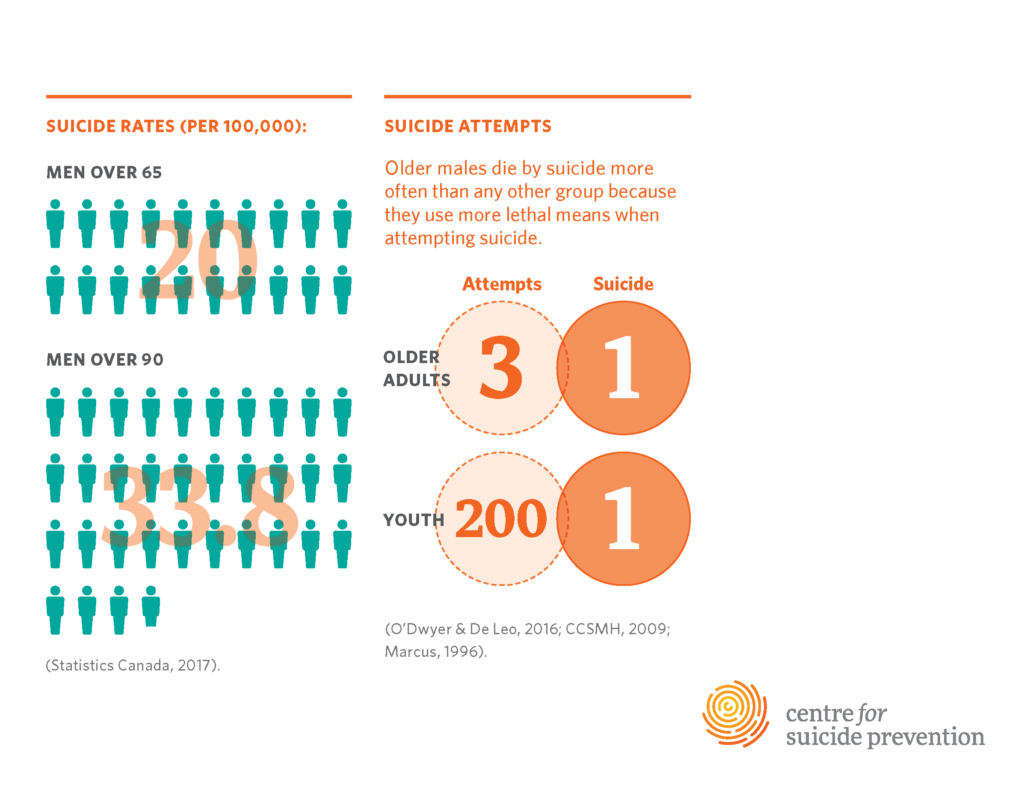
Understanding the High Suicide Rates in Older Adults
The alarming reality is that older adults, particularly those aged 75 and over, experience the highest suicide rates compared to any other age group. This demographic often faces multiple health challenges, including chronic illnesses and mental health issues that can exacerbate feelings of hopelessness. Factors such as social isolation and loneliness further contribute to a decrease in their overall mental health, leading to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Understanding the nuances of mental health in seniors is crucial in addressing this pressing public health concern.
Not only do older adults frequently battle physical health issues, but they also often encounter stigma, both from society and within their own families. This stigma can inhibit them from seeking help or discussing their mental health struggles, leading to a perilous buildup of despair. Furthermore, the lack of targeted resources for suicide prevention for older adults represents a significant gap in healthcare. The urgent need to raise awareness and increase support systems for this vulnerable population is paramount in reducing these tragic rates.
The Gap in Suicide Prevention Resources
Despite the high suicide rates among older adults, there is a concerning scarcity of effective support and resources tailored specifically for this age group. Major national suicide prevention organizations often fail to provide comprehensive resources directed toward older adults, which is a significant oversight given the unique characteristics of this demographic. Research conducted by experts in geriatric psychiatry indicates that online resources aimed at helping seniors with suicidal thoughts are limited and not easily accessible.
Creative solutions are necessary to bridge the gap in resources available for elderly suicide prevention. This includes developing targeted campaigns that raise awareness among organizations, clinicians, and community members about the distinct needs of older adults suffering from mental health issues. Improving access to online resources for seniors is essential; these resources must not only address suicidal ideation but also foster mental wellness, emphasizing the importance of social connections and community support.
Furthermore, studies suggest that enhancing accessibility to information can lead to earlier intervention and reduced stigma surrounding mental health among seniors. By integrating resources that focus on suicide prevention for older adults into well-known platforms, we can provide them with the information and support they desperately need.
The Role of Geriatric Psychiatry in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in addressing the unique mental health challenges faced by older adults, especially in the context of suicide prevention. These specialists understand the complexities of aging, including the interplay between physical health, mental well-being, and the social factors that contribute to increased suicide risk. By focusing on comprehensive assessments and providing tailored treatments, geriatric psychiatrists can effectively navigate the mental health landscape for seniors.
Their expertise is invaluable in developing and implementing targeted suicide prevention strategies that emphasize empathy-driven care and inclusivity. Such approaches may include fostering supportive environments that encourage open discussions about mental health issues, which can help dismantle the stigma associated with seeking help. Collaborative efforts between geriatric psychiatrists, community organizations, and family members are essential to create a robust safety net that addresses the mental health needs of older adults.
Promoting Mental Health Awareness in the Elderly Population
Raising awareness about mental health issues among older adults is a vital step toward preventing suicide in this demographic. Much of the stigma surrounding mental health can be dismantled through education and open communication. Community initiatives can be designed to increase public knowledge of mental health in seniors and the available resources for support, effectively reducing the barriers that prevent many from seeking help.
Furthermore, emphasizing the importance of mental health literacy can empower older adults to recognize their own symptoms and understand the need for professional help. Creating spaces in community centers or senior living facilities where seniors can engage in conversations about mental health can also play a critical role. By fostering an open dialogue, society can encourage more older adults to utilize available resources and improve their overall quality of life.
Utilizing Online Resources for Suicide Prevention
As internet usage among older adults continues to rise, the potential for using online resources in suicide prevention becomes increasingly significant. However, many seniors face challenges in navigating these platforms due to a lack of user-friendly materials tailored to their specific needs. Therefore, enhancing the accessibility and visibility of online suicide prevention resources designed with seniors in mind can make a substantial difference.
Efforts should focus on creating straightforward, easy-to-navigate websites and resources that offer practical guidance on mental health issues. Engaging content, including videos, testimonials, and interactive tools, can help capture the interest of older adults. Moreover, ensuring that these resources are readily available through reputable platforms can further facilitate access and empower seniors to seek the support they require without hesitation.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Elderly Mental Health
Social isolation is a significant risk factor contributing to the higher rates of suicide among older adults. Many seniors experience loneliness due to various factors such as losing loved ones, retirement, and limited mobility, which can lead to a decline in mental health. It is critical to address these social determinants by creating community programs that foster connection and engagement among older adults.
Innovative solutions, such as senior meetup groups or volunteer opportunities, can provide platforms for older adults to interact and build meaningful relationships. By mitigating feelings of isolation, we can create a supportive network that encourages individuals to share their experiences and seek help when needed, ultimately reducing their risk of suicide.
Funding and Research in Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
In order to effectively combat the rising suicide rates among older adults, there is a pressing need for increased funding and targeted research initiatives. Government agencies, along with private foundations, must prioritize mental health research that focuses specifically on the elderly population. By directing resources toward understanding the unique mental health challenges faced by seniors, we can develop more effective prevention strategies.
In addition, funding can support community-based programs that are designed to specifically meet the needs of older adults. These initiatives can enhance public awareness of available resources for elderly suicide prevention and facilitate access to mental health services tailored to seniors, ultimately improving outcomes for this vulnerable population.
Creating Tailored Campaigns for Mental Health Resources
To truly address the disparities in mental health resources available for older adults, tailored campaigns are essential. These campaigns should focus on understanding the specific needs of seniors and providing clear, concise information about available support services. Whether through public health initiatives, educational materials, or community outreach programs, creating targeted resources can significantly improve mental health outcomes.
Collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations is critical in developing these tailored campaigns. By leveraging the expertise of those who specialize in geriatric psychiatry and mental health, we can craft messages and programs that resonate with older adults, ultimately encouraging them to seek the help they need.
The Importance of Family Support in Elderly Mental Health
Family plays a pivotal role in the mental health of older adults, often serving as the first line of support in times of crisis. Families should be educated on the signs of mental health issues and suicide risk to effectively support their elderly loved ones. By fostering open communication, families can create an environment in which seniors feel supported and empowered to discuss their feelings, fears, and mental health challenges.
Moreover, involving families in the suicide prevention conversation can help dismantle the stigma associated with mental illness, encouraging openness about seeking help when needed. Providing families with resources and knowledge about mental health can positively impact not only the individual but the entire household, creating a more supportive atmosphere for older adults facing mental health struggles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective resources for elderly suicide prevention?
Effective resources for elderly suicide prevention include community mental health services, geriatric psychiatry practices, and national helplines specializing in mental health in seniors. Programs designed for older adults focus on addressing their unique challenges, such as isolation and depression. Online resources can also provide information on local support groups and hotlines aimed specifically at the elderly population.
Why are suicide rates in elderly individuals increasing?
Suicide rates in elderly individuals are increasing due to factors such as social isolation, the loss of loved ones, chronic health conditions, and depression. The rise is particularly noted in adults aged 75 and over, highlighting the importance of targeted mental health support and resources for elderly suicide prevention.
How does geriatric psychiatry address suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry addresses suicide prevention for older adults by focusing on the unique mental health needs of seniors. Specialists in this field develop tailored interventions and programs that consider the factors affecting mental health in seniors, such as cognitive decline and social isolation. They work to ensure that preventive measures are both effective and easily accessible.
What online resources are available for seniors facing suicidal thoughts?
There are several online resources available for seniors facing suicidal thoughts, including dedicated websites from mental health organizations that offer information on coping strategies, crisis intervention, and support directories. Important platforms include the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline and resources specific to elderly suicide prevention, which provide valuable information and assistance.
What role does social isolation play in suicide prevention for older adults?
Social isolation is a critical factor in suicide prevention for older adults, as it can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression. Addressing social isolation through community engagement programs and support networks can significantly reduce suicide rates in this demographic, emphasizing the need for initiatives that foster social connections among seniors.
How can families help with suicide prevention for older adults?
Families can help with suicide prevention for older adults by maintaining open lines of communication, encouraging social interactions, and providing emotional support. It is essential for families to recognize warning signs such as withdrawal or changes in behavior, and to seek professional help from geriatric psychiatry when necessary.
What are the signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults?
Signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults can include expressions of hopelessness, withdrawal from social activities, changes in mood or behavior, and increased talking about death or dying. Recognizing these signs is crucial for effective suicide prevention and can prompt timely intervention.
Are there specific campaigns targeting mental health in seniors?
Yes, there are specific campaigns targeting mental health in seniors that focus on raising awareness about depression and suicide risks in older adults. These campaigns aim to promote available resources for elderly suicide prevention and address the stigma associated with seeking help.
Why is there a lack of resources for elderly suicide prevention?
The lack of resources for elderly suicide prevention is attributed to systemic biases against older adults, underrepresentation in research, and the historical focus of mental health campaigns on younger populations. This highlights the urgency for organizations to develop initiatives that address the specific needs of seniors.
What can communities do to improve elderly suicide prevention?
Communities can improve elderly suicide prevention by developing local support programs, enhancing mental health services for seniors, and fostering social inclusion through community events and activities. Collaborating with geriatric specialists to create tailored resources will also enhance the accessibility and effectiveness of prevention efforts.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Suicide Risk | Older adults, especially those aged 75 and above, have the highest suicide rates among all age groups. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations provide limited resources for older adults, creating an imbalance. |
| Research Findings | A study by McLean Hospital revealed that older adults face significant challenges when searching for online suicide prevention resources. |
| Rising Rates | Suicide rates in adults over 75 have increased, contrary to trends in younger age groups. |
| Need for Targeted Campaigns | Experts emphasize the need for tailored suicide prevention initiatives that address the unique circumstances of older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that demands immediate attention. The alarming statistics reveal that individuals aged 75 and older experience the highest rates of suicide, yet resources aimed at assisting them are shockingly scarce. To combat this growing crisis, it is essential to develop tailored suicide prevention programs and campaigns that adequately address the specific needs of this vulnerable population. By enhancing access to information and support, we can work towards reducing these preventable tragedies and ensuring that older adults receive the help they need.