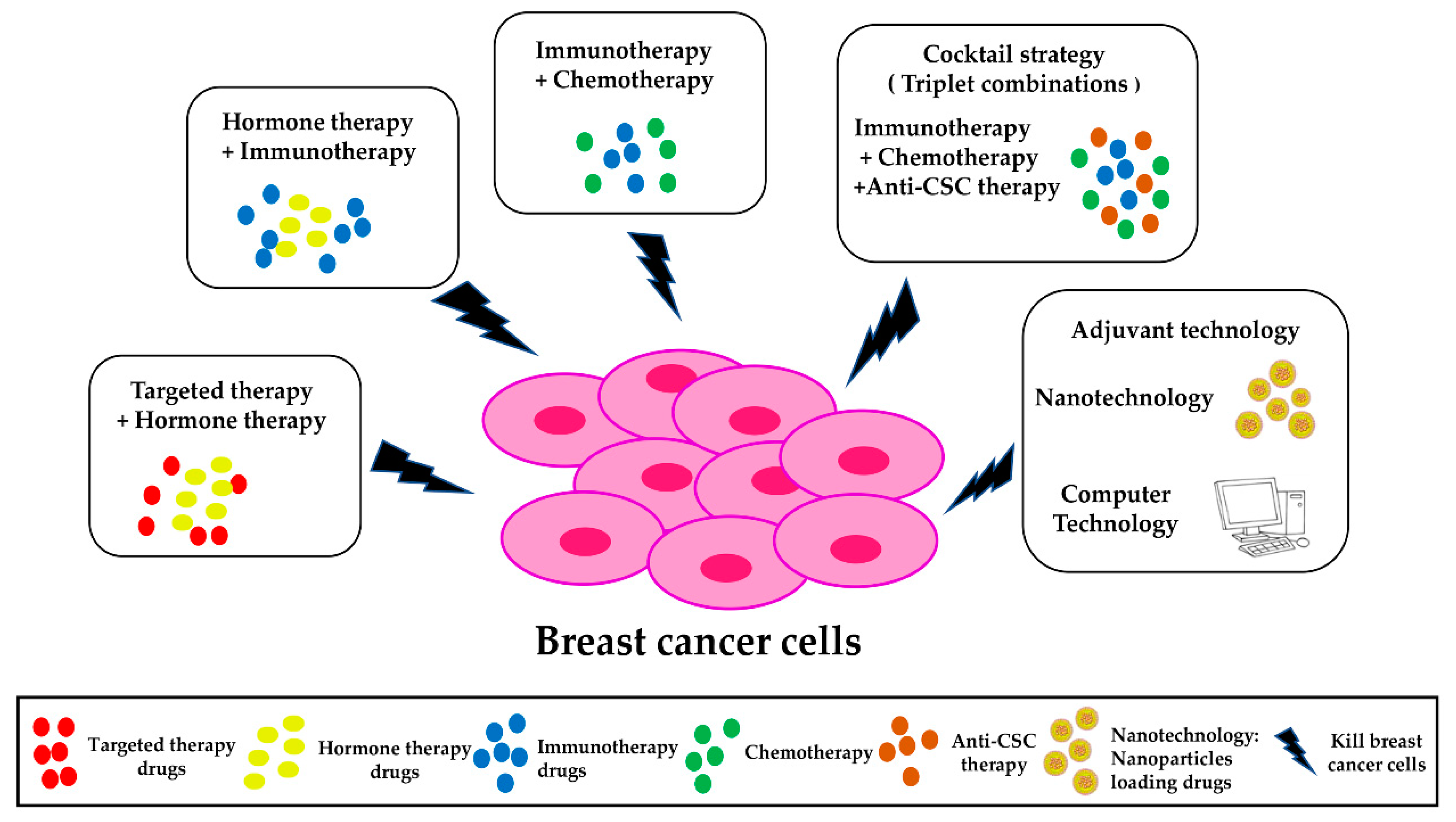
Molecular therapies for cancer present a transformative approach in the realm of cancer research. These innovative treatments are designed to target the specific aberrations that drive cancer’s uncontrollable growth, allowing for highly personalized and effective strategies to combat various forms of the disease. Recent advances have shed light on the role of molecular glues, which facilitate critical protein interactions disrupted by genetic mutations in cancer cells. These therapies harness inherent biological mechanisms, paving the way for novel targeted cancer treatments that could redefine patient outcomes. By pushing the boundaries of our understanding of protein interactions, molecular therapies are setting the stage for a new paradigm in addressing the complexities of cancer.
Cancer treatment has evolved dramatically with the advent of targeted molecular therapies that focus on specific biological pathways involved in tumor growth. By utilizing small molecules that act as molecular glues, researchers aim to bridge the gaps in protein interactions disrupted by genetic abnormalities. This approach not only enhances the effectiveness of treatments but also minimizes side effects by leaving healthy cells unharmed. As scientists unravel the intricacies of protein interactions and the effects of genetic mutations in cancer, a new era of tailored therapies is emerging, offering hope and improved outcomes for patients battling various forms of cancer.
The Promise of Molecular Therapies for Cancer Treatment
Molecular therapies have emerged as a beacon of hope in the ongoing battle against cancer, targeting the disease at its molecular roots rather than just treating symptoms. By focusing on specific genetic mutations and the associated protein interactions, researchers have made substantial progress in developing therapeutic interventions like molecular glues. These therapies aim to understand not just what happens in cancer cells, but why and how, allowing for a more tailored and effective treatment strategy.
Recent advancements in molecular therapies underscore the significance of targeted approaches. By disrupting the uncontrollable proliferation of cancer cells through the manipulation of protein interactions, innovative treatments can potentially offer greater efficacy with fewer side effects compared to traditional cancer therapies. This nuanced understanding of molecular interactions is imperative for the development of less toxic and more specific cancer treatments, paving the way for a new era in oncology.
Understanding Genetic Mutations in Cancer
Genetic mutations play a pivotal role in the development and progression of cancer, acting as triggers for uncontrolled cell growth and division. They alter the normal function of proteins that manage critical cellular processes, leading to phenotypic changes that characterize cancerous cells. Research into these mutations reveals their complexity, where even minor alterations can result in significant disruptions in protein networks, highlighting the urgent need for continued studies in cancer genetics and the potential for therapies that can restore normal protein function.
Notably, investigating specific mutations, such as those in the KBTBD4 protein, has provided crucial insights into how these aberrations contribute to cancer pathology. This exploration helps scientists identify potential therapeutic targets by revealing how these mutations affect molecular interactions within the cell. Understanding these mechanisms not only enhances our knowledge of cancer biology but also informs the development of targeted treatments that can directly address the underlying genetic causes of the disease.
Molecular Glues: Revolutionizing Targeted Cancer Treatments
Molecular glues represent a groundbreaking class of therapeutics designed to mediate previously unrecognized protein interactions within cancer cells. By facilitating interactions between proteins that normally do not bind, these small molecules have the potential to trigger cellular processes that lead to the degradation of harmful proteins associated with cancer development. This approach provides a new dimension to drug design, as it opens up avenues for targeting proteins deemed “undruggable” by traditional methods.
The ability of molecular glues to reshape protein interactions emphasizes their therapeutic versatility. For example, the molecule UM171 has shown promise in targeting the CoREST complex, a vital component in gene regulation. By cleaving maladaptive protein interactions, researchers are unveiling strategies that can effectively disrupt cancer pathways. As this field evolves, molecular glues could redefine how oncologists approach therapy, moving from a one-size-fits-all strategy to more precise, individualized treatments based on the unique genetic landscape of a patient’s cancer.
Protein Interactions and Their Role in Cancer
Understanding protein interactions is integral to comprehending cancer biology, as these relationships dictate numerous cellular functions, including growth and apoptosis. The dysregulation of these interactions often leads to malignant transformations. Recent research has underscored the importance of exploring how different proteins collaborate within oncogenic pathways, as this knowledge is key in devising targeted interventions that can inhibit or modify these pathways.
Research focusing on specific interaction networks within cancer cells has revealed that targeting these complexes could provide a novel approach to therapy. By identifying which interactions can be altered or disrupted, scientists can tailor treatment options that more effectively combat malignancies based on their molecular characteristics. This strategic focus on protein interactions not only enhances our understanding of cancer progression but also aids in the identification of new drug targets for molecular therapies.
Innovation in Cancer Research
The ongoing evolution of cancer research signifies a shift towards more innovative, molecularly-based strategies for understanding and treating the disease. With advancements in technology, researchers can now dissect the complex biological networks that underpin cancer development at a level of detail previously unattainable. This involves not only identifying genetic mutations but also scrutinizing their implications on protein behavior and cellular pathways.
As research continues to unfold, the integration of cutting-edge methodologies such as cryo-electron microscopy provides unprecedented insights into the structural and functional aspects of proteins associated with cancer. These advancements are making it possible to visualize how molecular glues and mutations interact on an atomic scale, forging paths toward more precise therapeutic approaches that could revolutionize the treatment landscape and significantly improve patient outcomes.
The Future of Targeted Cancer Therapies
Looking ahead, the future of targeted cancer therapies appears bright, as the principles of molecular therapy continue to mature. Researchers and clinicians are increasingly focused on personalized medicine, aiming to tailor treatments based on individual genetic profiles. Advances in understanding molecular glues and their ability to manipulate protein interactions are paving the way for innovative therapies that are not only more effective but also safer, minimizing the side effects commonly associated with traditional treatments.
Moreover, as scientists uncover the intricacies of genetic mutations in various cancer types, they can better predict how tumors will respond to specific therapies. The potential for molecular therapies to reshape our understanding of resistance mechanisms in cancer treatments is significant. Continuous exploration in this field promises to enhance the quality of life for patients and could lead to groundbreaking alternatives in cancer management.
Cross-disciplinary Collaboration in Cancer Research
The complexity of cancer necessitates interdisciplinary collaborations among chemists, biologists, and clinicians to advance the frontiers of cancer research. These collaborative efforts are crucial in bridging the gap between basic science and clinical applications, allowing researchers to translate laboratory discoveries into real-world treatments. By working together, scientists can combine their expertise to tackle the multifaceted nature of cancer more effectively.
For instance, the integration of knowledge from molecular biology and chemical design has led to significant breakthroughs in understanding drug-target interactions at a molecular level. This synergy enables the development of more targeted and effective cancer therapies, including the design of novel molecular glues that specifically address genetic mutations within tumors. Such collaborative approaches are likely to accelerate innovations, driving the discovery of new treatments that could transform cancer care.
The Importance of Research Funding in Cancer Therapies
Adequate research funding is essential for advancing the field of molecular therapies for cancer. Investments from governmental institutions like the National Institute of Health significantly bolster the capabilities of research teams, allowing them to explore groundbreaking ideas that may lead to transformative treatments. Financial support enables resources to be directed toward innovative research projects, expanding our understanding of cancer biology and fostering the development of targeted therapies.
Furthermore, funding facilitates collaboration across institutions, thereby enhancing research efforts. With the backing of comprehensive funding initiatives, laboratories are empowered to carry out comprehensive studies that address critical challenges in cancer therapeutics, including the identification of effective molecular glues and understanding genetic mutations. This financial commitment ultimately translates into scientific advancements that could offer hope to millions affected by cancer.
Patient-Centric Approaches in Cancer Research
A growing focus on patient-centric approaches is reshaping cancer research, emphasizing the importance of involving patients in their treatment decisions and research initiatives. By prioritizing patient needs and preferences, researchers are gaining valuable insights that can inform the direction of study and the type of therapies being developed. This shift not only enhances the relevance of research but also ensures that emerging therapies meet the actual needs of those living with cancer.
Moreover, incorporating patient perspectives into research can lead to the identification of novel therapeutic targets based on real-world experiences and outcomes. This collaborative model fosters a deeper understanding of how molecular therapies can integrate into patient care effectively, ensuring that new treatments are both scientifically sound and genuinely beneficial. Ultimately, centering cancer research around patients is expected to yield more successful outcomes and improve the overall quality of life for individuals battling the disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are molecular therapies for cancer and how do they work?
Molecular therapies for cancer are innovative treatments that use small molecules to target specific genetic mutations and protein interactions within cancer cells. These therapies, such as molecular glues, disrupt the uncontrolled growth of cancer by altering protein interactions, making it possible to target undruggable proteins traditionally resistant to treatment.
What role do genetic mutations play in molecular therapies for cancer?
Genetic mutations are pivotal in molecular therapies for cancer, as they can create abnormal protein interactions that drive cancer progression. By understanding these mutations, researchers can design targeted therapies that either mimic the effects of molecular glues or correct the dysfunctional interactions caused by mutations.
How do molecular glues contribute to targeted cancer treatments?
Molecular glues facilitate essential interactions between proteins that normally do not bind, leading to the degradation of disease-causing proteins. This mechanism allows for effective targeting of proteins involved in cancer growth, providing a new avenue for developing targeted cancer treatments with improved specificity.
What are some promising findings from recent cancer research on molecular therapies?
Recent cancer research has highlighted the discovery of small molecules, like UM171, that act as molecular glues to disrupt critical protein complexes in cancer cells. These findings enhance our understanding of how small molecules can influence genetic mutations and protein interactions, paving the way for more effective molecular therapies.
Can molecular therapies for cancer be applied beyond oncology?
Yes, the principles behind molecular therapies for cancer, such as targeting specific protein interactions and understanding genetic mutations, may extend to other diseases. The research into molecular glues and the chemical genetic convergence has the potential to reshape treatment strategies across various medical fields.
What innovations are being explored in the field of molecular therapies for cancer?
Innovations in molecular therapies for cancer include the development of new molecular glue compounds and advanced imaging techniques like cryo-electron microscopy, which provide detailed insights into how genetic mutations alter protein structures and functions, ultimately leading to novel therapeutic approaches.
Why are targeted cancer treatments considered a significant advancement in cancer therapy?
Targeted cancer treatments, including molecular therapies, represent a significant advancement because they offer personalized approaches that focus on the unique genetic makeup of a patient’s tumor. This specificity reduces side effects and enhances treatment efficacy compared to traditional chemotherapy, which affects both healthy and cancerous cells.
What challenges do researchers face in developing molecular therapies for cancer?
Researchers encounter challenges in discovering effective molecular glues and understanding the complex nature of protein interactions and genetic mutations in cancer. Identifying targetable mutations and designing small molecules that can effectively alter these interactions poses a significant hurdle in developing successful molecular therapies.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Research Focus | The studies focus on developing molecular therapies that disrupt cancer growth by targeting protein interactions. |
| Molecular Glues | Molecular glues are small molecules that facilitate interactions between typically non-interacting proteins, leading to targeted degradation of disease-causing proteins. |
| Key Findings | The study identified how UM171 modifies protein interactions and how mutations in the KBTBD4 protein disrupt these processes, highlighting potential new treatment pathways. |
| Research Implications | The research paves the way for innovative drug designs that target previously considered ‘undruggable’ proteins and suggests collaborations between genetic findings and chemical design. |
Summary
Molecular therapies for cancer represent a groundbreaking advancement in oncology, aiming to specifically target and disrupt cancer cell growth at the molecular level. Through innovative studies, researchers have identified how molecular glues and genetic mutations influence cancer-related protein interactions, offering promising pathways for treatment. As this research progresses, it not only underscores the potential of molecular therapies to revolutionize cancer treatment but also hints at broader applications in combating various diseases.