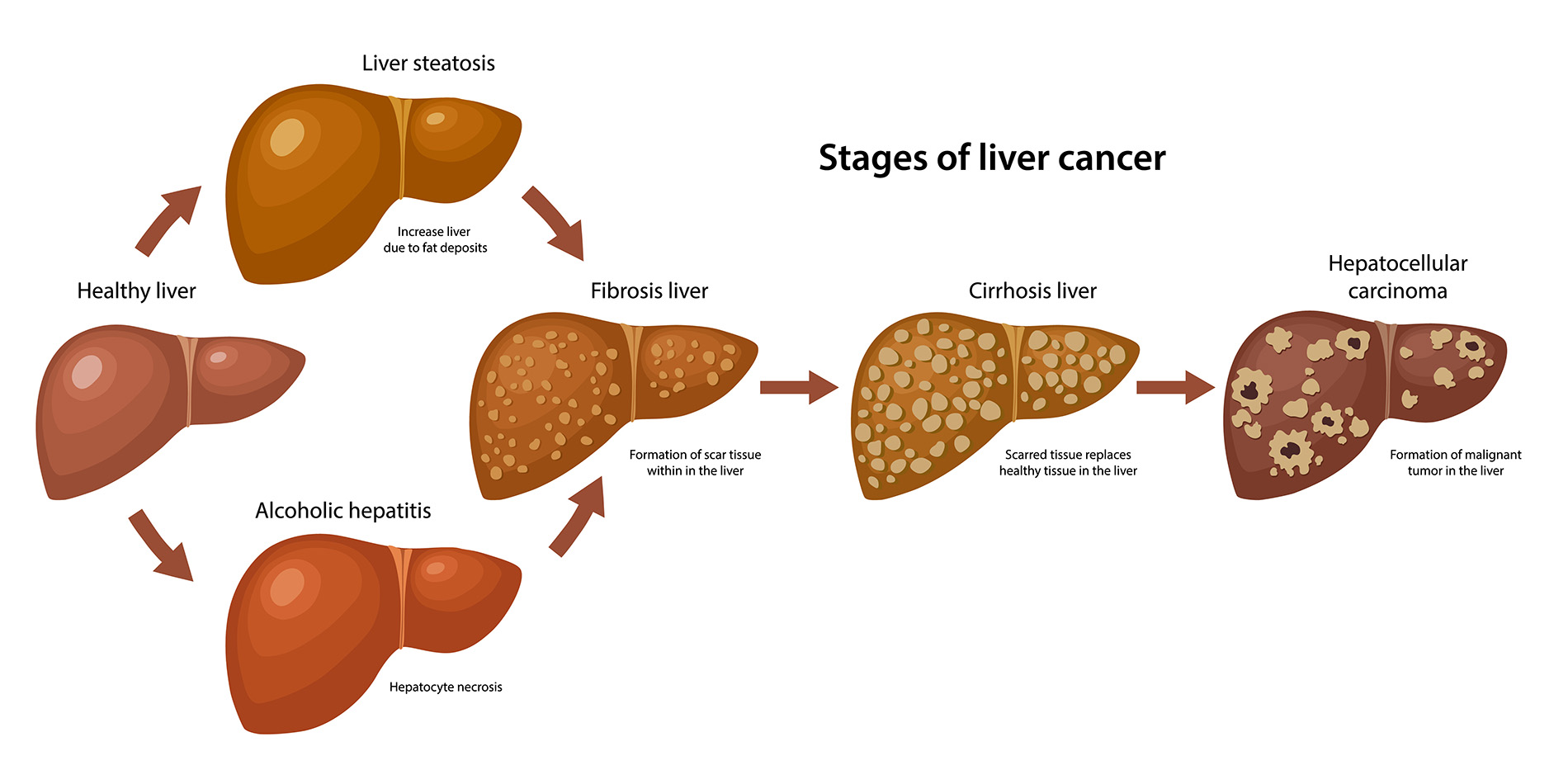
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is an emerging focus in recent liver disease research, highlighting how disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. A crucial study published in Nature Communications has unveiled a significant molecular switch that regulates bile acids, suggesting new avenues for liver cancer treatment. Bile acids, which aid in fat digestion, also serve important roles in metabolism, making their balance essential for liver health. When upset, these imbalances not only lead to liver injury but also promote inflammatory processes that may accelerate cancer development. Understanding the interplay between bile acid metabolism and cellular pathways like YAP FXR signaling could pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies to combat liver cancer.
The link between bile fluid irregularities and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has gained attention as researchers delve into the intricate mechanisms behind liver health and disease. Imbalances in bile salts can act as catalysts for serious conditions, including various forms of liver cancer. Recent findings suggest that the regulation of bile acids and their metabolic effects are pivotal in therapeutic developments for liver ailments. YAP FXR signaling emerges as a critical player, emphasizing the necessity of maintaining healthy bile acid levels to prevent liver damage and malignancy. As liver disease researchers continue to uncover these relationships, the potential for effective liver cancer treatments becomes increasingly promising.
Understanding Bile Imbalance in Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance is a critical factor in the development of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, produced by the liver, are essential for fat digestion and absorption, but when their metabolism is disrupted, it can lead to serious consequences, including liver cancer. Recent research has highlighted that the improper regulation of bile acids can trigger inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately escalating to HCC. The discovery of a key molecular switch that influences bile acid metabolism offers insights into how we might better address liver cancer treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Furthermore, understanding the mechanisms behind bile acid metabolism is essential for developing targeted therapies for liver cancer. The Hippo/YAP pathway has been identified as an important regulator in this context. By inhibiting the repressor activity of YAP, researchers aim to restore the balance of bile acids, minimizing liver damage and potentially halting cancer progression. These findings underscore the need for continued research in liver disease focusing on bile acids and their regulatory pathways, as they may lead to innovative strategies for HCC treatment.
The Role of YAP and FXR in Bile Acid Metabolism
The study of YAP (Yes-associated protein) and FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) offers a promising avenue for understanding bile acid metabolism in liver cancer. YAP, typically linked to cell growth and proliferation, surprisingly acts to inhibit FXR’s function, causing an accumulation of bile acids that contribute to liver inflammation and cancer. This intricate relationship suggests that targeting YAP or enhancing FXR function could be pivotal in restoring bile acid balance and preventing liver disease progression. Mechanisms that disrupt the regulatory role of FXR must be explored further, as they hold great potential for liver cancer therapies.
Research into this signaling pathway is crucial for advancing liver disease treatment. By activating FXR or blocking YAP’s repressive functions, it may be possible to mitigate the adverse effects associated with bile acid overproduction. As liver disease research continues to evolve, understanding the interplay between YAP and FXR in bile acid metabolism could lead to groundbreaking interventions in liver cancer treatment, offering hope where previous therapies have fallen short.
Implications for Liver Disease Research
The implications of these findings extend beyond just liver cancer; they provide a broader understanding of liver disease mechanisms. By identifying how bile acid imbalance leads to conditions like fibrosis and HCC, researchers can map out a more comprehensive approach to liver disease research. This also encourages the exploration of new therapeutic strategies that can modulate bile acid levels and improve liver function, initiating a more proactive approach in managing liver health.
Moreover, these insights may influence ongoing studies in related fields, such as metabolic disorders and chronic liver disease. Integrating knowledge about bile acid metabolism and its effects on liver pathology can open new doors for interdisciplinary research. Collaborations focusing on cell signaling and metabolic regulation are essential to enhance our understanding and create effective interventions for various liver diseases, including advanced liver cancer.
Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Liver Cancer Treatment
Given the critical role of bile acids in liver cancer progression, novel therapeutic approaches focusing on bile acid metabolism are emerging. By leveraging the understanding of FXR and its relationship with YAP, researchers can develop pharmacological agents that specifically target these pathways. Potential therapies may not only aim to enhance FXR activity but also include strategies to augment bile acid excretion, effectively reducing liver toxicity and inflammation associated with HCC.
Additionally, a holistic approach incorporating lifestyle modifications alongside pharmacological treatments may yield beneficial effects. Dietary changes that promote healthy bile composition and function could complement innovative therapies, leading to enhanced patient outcomes. As we advance in liver cancer treatment, integrating tailored solutions based on bile acid dynamics may significantly impact the management and prognosis of liver cancer patients.
Clinical Trials and Future Directions
The exploration of bile acid metabolism in the context of liver cancer treatment has sparked interest in clinical trials aimed at testing compounds that enhance FXR activity. These compounds are designed to restore bile acid balance, counteract inflammation, and potentially reduce tumor growth in HCC patients. Healthy progression from laboratory findings to clinical application is critical, as it allows researchers to validate their hypotheses in real-world scenarios.
Future directions in liver disease research should emphasize collaborative efforts that bring together molecular biologists, oncologists, and clinicians. By pooling expertise, we can create a robust pipeline for translating laboratory discoveries, such as the role of bile acids in liver cancer, into effective treatments that address patient needs. Continuous monitoring of clinical outcomes will provide invaluable feedback, shaping the course of future research and treatment strategies in liver cancer and associated liver diseases.
The Importance of Bile Acids in Metabolism
Bile acids are more than just emulsifiers; they serve as essential signaling molecules that regulate various metabolic pathways in the liver. Their roles extend beyond digestion to include influences on energy balance, glucose metabolism, and the body’s overall metabolic homeostasis. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to significant implications for liver health, making it essential for researchers to delve into these metabolic pathways.
Understanding how bile acids participate in cellular signaling provides critical insights into liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. As the field of liver disease research evolves, a focus on the intricate relationships between bile composition, metabolic health, and liver functionality will be crucial in identifying new biomarkers for early detection and intervention, inevitably leading to improved treatments for liver cancer.
Investigating Bile Acid Metabolism Pathways
Investigating the pathways of bile acid metabolism sheds light on the interconnected roles of various factors influencing liver health. The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, specifically, shows promise in regulating bile acid levels and signaling, indicating that disturbances in this pathway could significantly impact liver disease susceptibility. Research concerning bile acids and their receptors opens the door for novel therapeutic options directed at restoring balance in liver function, especially in conditions leading to HCC.
Ongoing studies that utilize both genetic and molecular approaches to examine bile acid metabolism will provide deeper insights into the potential for targeted therapies. By comprehensively analyzing how bile acids affect liver disease inflammation and cancer progression, researchers can develop more refined strategies that address the underlying causes of liver cancer rather than merely managing symptoms.
Bile Acid Excretion and Liver Cancer Prevention
The process of bile acid excretion plays a vital role in maintaining liver health and could be a key factor in liver cancer prevention. It is crucial for eliminating excess bile acids that may otherwise accumulate and lead to liver damage or malignancy. Understanding the mechanisms that facilitate bile acid export, such as the role of BSEP (Bile Salt Export Pump), can offer insights into how we might bolster these pathways therapeutically.
Enhancing bile acid excretion may not only help prevent the detrimental effects associated with their excess but also provide a pathway for reducing the risk of liver cancer in individuals predisposed to liver disease. Ongoing research into medications or lifestyle changes that increase bile acid clearance from the liver could be instrumental in advancing preventive strategies, ultimately promoting liver health and addressing HCC risk more effectively.
Collaboration in Liver Disease Research
Collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and institutions is crucial for effectively addressing the challenges posed by liver diseases such as cancer. Different research perspectives contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues like bile imbalance and its effects on liver health. By fostering interdisciplinary partnerships, the field can better leverage the expertise from various areas of study, including molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical medicine.
Shared resources and knowledge exchange are essential to enhance the pace of liver disease research. Collaborative efforts can facilitate large-scale clinical trials, improve data collection, and lead to the development of multifaceted approaches to treatment that consider individual patient needs and disease mechanisms. By prioritizing collaboration, we increase the chances of discovering effective liver cancer treatments that can significantly impact patient lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of bile acids in liver cancer treatment?
Bile acids are crucial components in liver cancer treatment as they are linked to bile imbalance, which can trigger liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent research highlights how disturbances in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and cancer progression, emphasizing the need for therapies targeting bile acid regulation.
How does bile imbalance contribute to the progression of liver cancer?
Bile imbalance contributes to liver cancer progression by causing an accumulation of bile acids in the liver, leading to inflammation and fibrosis. This is primarily due to the action of YAP, which interferes with FXR, the bile acid sensor, promoting overproduction of bile acids that fosters a tumor-friendly environment.
What is the significance of FXR in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
FXR, or Farnesoid X receptor, plays a crucial role in bile acid metabolism. In liver cancer, particularly HCC, YAP acts as a repressor of FXR, disrupting bile acid homeostasis. Targeting FXR activation may provide therapeutic avenues to restore normal bile acid levels and mitigate cancer progression.
Can enhancing bile acid excretion be a treatment option for liver cancer?
Yes, enhancing bile acid excretion can potentially serve as a treatment option in liver cancer by alleviating the toxic accumulation of bile acids in the liver, thereby reducing inflammation and the risk of cancer. This approach is part of ongoing research to identify effective liver cancer therapies.
What are the implications of YAP FXR signaling in liver disease research?
The implications of YAP FXR signaling in liver disease research are significant, as this pathway is linked to the regulation of bile acid metabolism and tumor formation. Understanding this signaling mechanism opens up new therapeutic targets for liver cancer treatment and highlights the need for continued research on bile imbalances.
How can pharmacological interventions targeting bile acids impact liver cancer prognosis?
Pharmacological interventions that target bile acids, such as FXR activators, can potentially improve liver cancer prognosis by restoring bile acid balance, reducing inflammation, and preventing fibrosis. Such strategies aim to disrupt the harmful cycle initiated by bile imbalance, offering hope for better treatment outcomes in liver cancer patients.
What research has been done on bile acids and their connection to HCC?
Research has demonstrated a critical connection between bile acids and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), revealing that an imbalance in bile acid production can lead to liver injury and promote cancer development. Studies are ongoing to explore how regulating bile acid metabolism can inform treatment strategies for HCC.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | Imbalance in bile acids can lead to liver diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Molecular Switch Identified | A study identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile acids, which could lead to novel liver cancer treatments. |
| Role of Bile Acids | Bile acids are critical for fat digestion and also act like hormones in metabolic processes. |
| YAP and FXR Interaction | YAP inhibits the bile acid sensor FXR, leading to bile acid accumulation and liver damage. |
| Potential Treatment Approaches | Modulating YAP and enhancing FXR function could provide new strategies for preventing liver cancer. |
| Research Implications | Findings may enhance understanding of metabolic control and nutrient sensing in liver biology. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a critical area of study, revealing how disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to severe liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A recent study highlights a crucial molecular switch that may pave the way for novel therapeutic interventions. Understanding the relationship between bile acids, cellular signaling, and liver health is vital for developing effective treatments against this prevalent form of cancer.