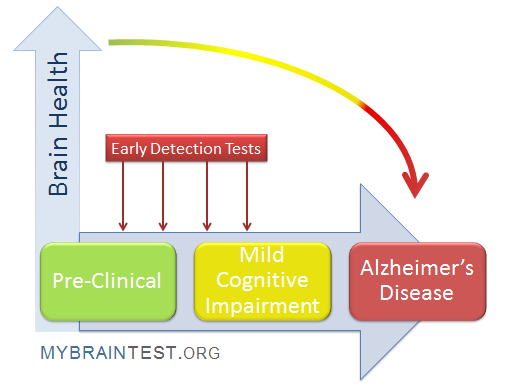
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for effective intervention and improved patient outcomes. Recent research indicates that olfactory testing, specifically a simple smell test for Alzheimer’s, could provide valuable insights in this regard. The study showcased how participants’ abilities to identify and differentiate odors at home can serve as an early indicator of cognitive impairment signs linked to Alzheimer’s risk. The findings emphasize the significance of recognizing subtle changes in our sense of smell as potential predictors of neurodegenerative diseases. By implementing such accessible screening methods, researchers aim to revolutionize the early identification and treatment of conditions like Alzheimer’s.
Identifying the early signs of Alzheimer’s can significantly alter the course of treatment and support for patients. Known as cognitive decline or impairment, early warnings may include a decreased ability to recognize scents, which can be assessed through innovative olfactory assessments. Such tests not only highlight early-stage neurodegenerative changes but also empower individuals to seek medical guidance sooner. Research in this area continues to unfold, presenting alternatives for understanding Alzheimer’s risk through a simple and non-invasive approach. As we delve deeper into this emerging field, the potential for proactive health solutions becomes increasingly evident.
Understanding the Role of Olfactory Testing in Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Recent advancements in olfactory testing have shown significant promise in the early detection of cognitive impairment, particularly in identifying individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. The sense of smell, often overlooked, has emerged as a critical indicator of neurodegenerative diseases. Researchers from Mass General Brigham revealed that simple smell tests could effectively identify cognitive decline before traditional memory symptoms manifest. By using odor labels placed on a card, participants can engage in a straightforward assessment of their ability to discriminate and identify different smells, providing actionable insights into their cognitive health.
The importance of early detection cannot be overstated, as intervening before symptoms appear may lead to more effective management of Alzheimer’s disease. This new at-home olfactory testing method is particularly beneficial, as it allows individuals to monitor their cognitive health in a familiar environment. As highlighted by the researchers, the correlation between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive impairment enhances the viability of using smell tests as a routine check-up for older adults. This approach not only increases accessibility but also fosters a proactive stance towards aging and health.
Identifying Alzheimer’s Risk Through Cognitive Impairment Signs
Identifying Alzheimer’s risk through observable cognitive impairment signs is paramount in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases. Many individuals may experience subtle changes in cognitive function that signal the onset of greater issues. The research conducted by Mass General Brigham emphasizes the value of recognizing these signs early on, particularly through olfactory testing, as they can serve as precursors to more severe symptoms of Alzheimer’s. By understanding and educating the public about these signs, families can collaboratively take steps towards seeking early interventions.
Furthermore, incorporating tests for cognitive impairment into routine healthcare can help facilitate early diagnosis and treatment. Professionals may consider combining traditional assessments with innovative techniques like smell tests to create a comprehensive evaluation of cognitive health. As neurodegenerative diseases progress, early identification through signs of cognitive decline is crucial for patient care. By establishing a baseline of an individual’s cognitive abilities, healthcare providers may be better positioned to track changes and adapt treatment plans accordingly.
Exploring Neurodegenerative Diseases Detection with New Methods
Researchers are continuously exploring new methods for neurodegenerative diseases detection, with olfactory testing gaining momentum as a feasible solution. The shift towards at-home evaluations offers a revolutionary approach, providing individuals with the tools they need for early detection while minimizing the need for extensive clinical visits. This is particularly significant for older adults who may find it challenging to access medical facilities. Through these innovative methods, individuals can take charge of their cognitive health and seek help when necessary.
The efficacy of using smell tests in detecting neurodegenerative diseases lies in their simplicity and the direct correlation found between olfactory function and cognitive abilities. By focusing on everyday experiences like the ability to recognize familiar scents, researchers can better understand the underlying mechanisms that drive cognitive impairment. Incorporating olfactory testing into routine assessments could aid in developing personalized treatment plans and contribute to larger efforts aimed at unraveling the complexities of diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and more.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research: Olfactory Testing as Standard Practice
The future of Alzheimer’s research looks promising, particularly with the integration of olfactory testing into standard practice. As studies continue to validate the significance of this method in early detection, it may become commonplace for healthcare providers to recommend smell tests as part of routine cognitive assessments for older adults. Embracing this non-invasive and cost-effective approach could revolutionize the landscape of Alzheimer’s research, enabling early interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Additionally, as the understanding of olfactory dysfunction grows, it may lead to the development of more comprehensive frameworks for monitoring cognitive health. Future research could focus on creating advanced olfactory test kits that can be easily distributed among varied demographics, ensuring that detection methods are accessible to all. With ongoing research and increased understanding of how smell relates to cognitive functions, the potential for preventing or delaying the onset of Alzheimer’s disease becomes a realistic goal.
Why Smell Tests Could Be Key in Alzheimer’s Prevention
The idea that smell tests could be key in Alzheimer’s prevention is gaining traction in scientific communities. Researchers have consistently noted that a decline in olfactory function often precedes more pronounced cognitive impairment symptoms. This makes smell tests an invaluable tool for monitoring those at risk of developing Alzheimer’s. Simple home-based tests that assess an individual’s ability to recognize and differentiate smells may offer an early warning signal, creating opportunities for timely interventions that can slow or prevent cognitive decline.
By shedding light on the connection between olfactory loss and Alzheimer’s, researchers aim to pave the way for innovative prevention strategies. As more studies confirm these findings, there could be a paradigm shift in how we perceive Alzheimer’s screenings. The reliance on olfactory testing could ensure that preventive measures are implemented far before clinical symptoms emerge, highlighting the importance of proactive health management in aging populations.
Enhancing Awareness of Cognitive Impairment Signs Among Seniors
Enhancing awareness of cognitive impairment signs among seniors is crucial in addressing Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Many older adults may not recognize the subtle signs of cognitive decline, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Public health campaigns focused on educating seniors about these early indicators—such as difficulty identifying familiar smells—can empower individuals to seek help sooner. A more informed community can foster earlier interventions, ultimately improving quality of life for those at risk.
Furthermore, involving caregivers and family members in these awareness efforts is equally important. By educating those around seniors about cognitive impairment signs, we create a support network that can effectively monitor changes in behavior or cognition. Combined efforts among the elderly, their families, and healthcare workers can lead to increased early detection rates, turning attention to proactive measures that address Alzheimer’s risks before they evolve into more significant health challenges.
Comparing Cognitive Ability Through Multilingual Olfactory Tests
Comparing cognitive ability through multilingual olfactory tests is another exciting avenue opened by recent research. The study conducted by Mass General Brigham demonstrated that participants, regardless of their primary language, could engage effectively in olfactory assessments. This suggests that olfactory testing can be utilized in diverse populations, ensuring that language barriers do not impede early detection of cognitive impairment. Such inclusivity in research is vital, as it allows for broader applications of these methods across varying demographics.
Moreover, implementing multilingual olfactory tests could enhance our understanding of how cognitive decline manifests in culturally varied groups. As the research expands to include different languages and cultural contexts, it may reveal unique insights into olfactory cognition and its relationship with neurodegenerative diseases. This informed approach cultivates a holistic view of health and wellness, emphasizing that cognitive assessments must be tailored to accommodate the diverse backgrounds of individuals.
The Importance of Non-Invasive Methods for at-Home Testing
The importance of non-invasive methods for at-home testing, particularly in cognitive assessments, cannot be overstated. As evidenced by the olfactory tests developed by researchers from Mass General Brigham, a non-invasive approach enables individuals to monitor their cognitive health comfortably and privately. This method alleviates the anxiety often associated with clinical tests and encourages more seniors to engage in their health management proactively.
Furthermore, at-home testing frameworks can drastically reduce the logistic and financial barriers that often deter individuals from seeking cognitive assessments. By facilitating easy access to testing tools, healthcare systems can enhance engagement and increase the likelihood of timely interventions for those demonstrating early signs of cognitive decline. Non-invasive at-home testing thus represents a significant advancement in the quest for effective early detection strategies against Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Clinical Implications of Olfactory Testing in Neurology
The clinical implications of olfactory testing in neurology are profound. As studies continue to affirm its utility in detecting early signs of Alzheimer’s, healthcare professionals may integrate olfactory assessments routinely into neurological evaluations. This practice not only allows for earlier diagnosis but also encourages a more comprehensive understanding of a patient’s cognitive health over time. Clinicians can utilize these tests as part of a broader assessment strategy, combining traditional cognitive evaluations with innovative methods to provide a well-rounded evaluation of neurological status.
Additionally, as more healthcare settings begin to adopt olfactory testing, the potential for standardization rises. Establishing a consistent approach to incorporating smell tests in clinical practice can lead to improved outcomes for patients at risk of neurodegenerative diseases. By seeking to identify cognitive impairment signs early through routine assessments, healthcare providers can be better prepared to enact preventative measures, ensuring a higher quality of care for those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of olfactory testing in Alzheimer’s early detection?
Olfactory testing plays a significant role in Alzheimer’s early detection by assessing an individual’s ability to identify, discriminate, and remember different odors. Research indicates that a decline in the sense of smell can be an early warning sign of cognitive impairment, allowing for the identification of individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s disease before memory symptoms appear.
How does the smell test for Alzheimer’s work?
The smell test for Alzheimer’s involves participants sniffing odor labels placed on a card to evaluate their olfactory abilities. This at-home test provides a non-invasive and cost-effective way to gauge cognitive health, particularly in older adults, as research shows that those with cognitive impairment score lower in odor identification and discrimination compared to their cognitively healthy peers.
What are cognitive impairment signs that might indicate Alzheimer’s risk?
Cognitive impairment signs indicating Alzheimer’s risk may include difficulties with memory, language, problem-solving, and other cognitive functions. The decline in the ability to identify and remember odors, as assessed through olfactory testing, can also serve as an early indicator of potential neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Can olfactory dysfunction be associated with neurodegenerative diseases detection?
Yes, olfactory dysfunction has been associated with neurodegenerative diseases detection. Studies suggest that subtle declines in the sense of smell may indicate the early stages of conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Olfactory testing could ultimately aid in the early identification of individuals at risk for these diseases.
Why is early detection of Alzheimer’s crucial?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s is crucial because it allows for timely interventions and supports planning for future care. Identifying cognitive impairment before significant memory symptoms arise can provide patients and families with valuable information and options for management, potentially slowing disease progression.
What advancements are being made in Alzheimer’s early detection research?
Recent advancements in Alzheimer’s early detection research include the development of at-home olfactory tests, which evaluate the sense of smell as an early marker for cognitive decline. This approach aims to make it easier for individuals to assess their risk for Alzheimer’s disease and participate in research studies focused on early intervention strategies.
What is the Aromha Brain Health Test?
The Aromha Brain Health Test is an olfactory assessment tool designed to measure smell identification, discrimination, and memory. Developed as part of Alzheimer’s early detection research, it provides a straightforward method for individuals to evaluate their cognitive health both at home and in clinical settings.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| At-Home Olfactory Test | Researchers developed a test where participants sniff odor labels to assess smell capacity. |
| Significance of Smell | The sense of smell may indicate cognitive impairment years before memory symptoms appear. |
| Study Findings | Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower on smell discrimination tests compared to healthy peers. |
| Cultural Inclusion | Participants were recruited in both English and Spanish, highlighting the test’s adaptability across languages. |
| Future Implications | Future studies could include assessments to predict cognitive decline over time using olfactory tests. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial for identifying individuals at risk of cognitive decline. Recent research highlights that an innovative at-home olfactory test can effectively assess smell discrimination abilities, serving as an early indicator of Alzheimer’s disease. This non-invasive, cost-effective test not only aids in early detection but also raises the potential for timely interventions. With ongoing studies to further validate these findings, olfactory testing could revolutionize the approach to diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases, enhancing the prospects for affected individuals.