Brain cancer in children, particularly pediatric gliomas, poses unique challenges that require innovative approaches to enhance childhood cancer care. Recent advancements in AI predictive modeling have shown promise in transforming how we understand and manage the risks associated with these brain tumors. By analyzing multitudes of brain scans over time, researchers have developed techniques like temporal learning, which improve the accuracy of cancer recurrence prediction. These developments are crucial, as they offer hope for reducing the stress and burden on young patients and their families during follow-up imaging procedures. Understanding and utilizing AI tools could lead to more effective and personalized treatment plans for children battling brain cancer.
Childhood brain tumors, specifically pediatric gliomas, have emerged as a critical area of focus in cancer research. The complexities involved in diagnosing and treating these tumors necessitate innovative technologies, including advanced AI systems that offer predictive insights. By employing methods such as temporal learning, healthcare professionals can forecast cancer recurrence with greater precision, ultimately enhancing the management of childhood cancer treatment. The ability to assess longitudinal data effectively allows for tailored care strategies, significantly easing the emotional toll on families. Furthermore, research advancements in this field are paving the way toward improved outcomes for young patients and better support mechanisms within the healthcare system.
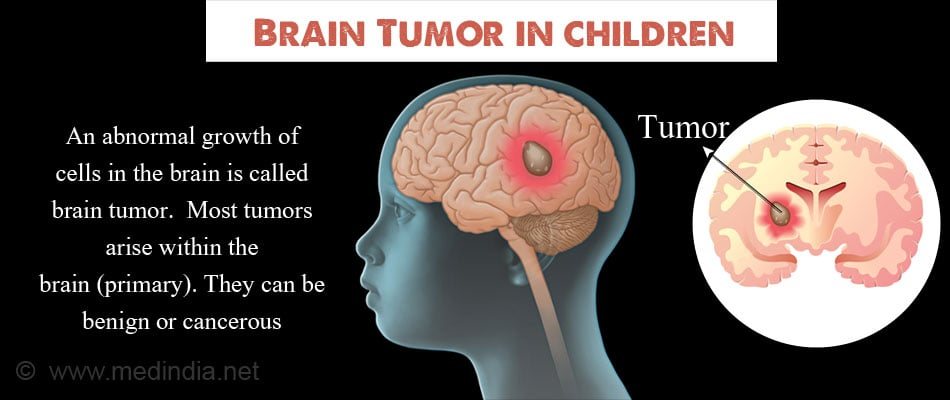
Understanding Brain Cancer in Children: Types and Challenges
Brain cancer in children, while relatively rare, presents unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Among the various forms of pediatric brain tumors, gliomas are particularly significant, as they comprise a notable portion of brain cancers diagnosed in children. These tumors can exhibit a wide range of behaviors, from highly aggressive to more indolent cases that may be cured with surgery. However, the unpredictability of recurrence looms over families as they navigate the aftermath of treatment. The need for ongoing surveillance creates stress, both for the pediatric patient and their parents, making it crucial to implement better predictive tools.
The evolving landscape of childhood cancer care emphasizes the importance of understanding the specific pathology of pediatric gliomas. As treatments have improved, so too have expectations for outcomes. Parents are increasingly focused on preventing relapse and ensuring their child remains healthy post-treatment. The ability to accurately assess the risk of recurrence is paramount, affording families peace of mind, and guiding medical professionals in making informed decisions about follow-up care.
The Role of AI in Predicting Cancer Recurrence in Pediatric Patients
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing cancer care, particularly in predicting the recurrence of gliomas in pediatric patients. Traditional imaging techniques often only provide a snapshot of the tumor’s status at a single point in time, which can lead to limitations in accurately assessing the risk of recurrence. The newly developed AI tools, utilizing advanced methods like temporal learning, evaluate multiple scans over time, thereby improving prediction accuracy and allowing for timely interventions. This represents a significant advancement in the landscape of pediatric cancer care, where precision and proactive measures are essential.
The recent study conducted at Mass General Brigham highlights the effectiveness of AI predictive modeling in identifying relapse risks among children with brain tumors. This innovative approach allows clinicians to hone in on the subtle changes that might indicate a recurrence, potentially decreasing unnecessary imaging for low-risk patients and prioritizing focused interventions for high-risk children. The integration of AI into clinical practice could significantly enhance the quality of life for these young patients and alleviate the emotional burden on their families.
Temporal Learning: A Breakthrough in Cancer Relapse Prediction
Temporal learning sets itself apart from traditional techniques by examining how a patient’s condition evolves over time based on sequential imaging. By analyzing a series of MRI scans, researchers are able to detect subtle changes that may signal a recurrence of brain cancer in children sooner than was previously possible. This innovative method addresses key limitations of conventional single-scan analysis, thus paving the way for more accurate predictions that are critical in the management of pediatric gliomas.
The integration of temporal learning into AI models demonstrates a significant leap forward, offering hope for improved outcomes in childhood cancer care. By leveraging a chronological array of scans, AI models can establish patterns and correlations that indicate the likelihood of recurrence. Although further validation is necessary before widespread clinical adoption, the promising results of this technique herald a new era of enhanced surveillance and personalized treatment plans for young patients battling brain cancer.
Childhood Cancer Care: Importance of Early Detection
The landscape of childhood cancer care fundamentally relies on timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment. Early detection has been shown to improve prognosis significantly, particularly for aggressive forms of gliomas. As research progresses towards novel predictive tools such as AI, the emphasis on catching brain cancer in children before it returns becomes increasingly paramount. This shift aims to transform standard care protocols, ensuring that children at high risk are monitored closely while minimizing the treatment burden on those deemed low risk.
With ongoing advancements in technology, the hope is that predicted relapse markers identified through AI will facilitate more efficient care strategies, enabling clinicians to tailor follow-up interventions to individual patient needs. That said, effective communication with families about these developments is essential to provide reassurance and support, contributing to a holistic approach to childhood cancer treatment that prioritizes both physical health and emotional wellbeing.
AI Predictive Modeling: Transforming Pediatric Cancer Surveillance
The advent of AI predictive modeling marks a transformative chapter in the world of pediatric cancer surveillance. By assessing diverse datasets, AI tools can generate insights that enhance clinical decision-making and improve patient outcomes. The ability to foresee potential relapses in pediatric gliomas enables healthcare providers to initiate more proactive measures, thereby optimizing the management of childhood brain cancers. This technological evolution redefines how pediatric oncology teams approach treatment and follow-up care.
By analyzing historical data from thousands of patient scans, AI models learn from the past to inform future predictions accurately. This approach is a game-changer, particularly as it reduces anxiety associated with frequent imaging while focusing resources on those who actually need intervention. As healthcare continues to embrace AI-driven strategies, families can expect a more nuanced, responsive approach to childhood cancer care that reaffirms the commitment to advancing treatment options for the youngest patients.
The Impact of Recurrence on Families: Emotional and Psychological Aspects
The recurrence of brain cancer in children doesn’t just affect the physical health of young patients; it also has profound emotional and psychological ramifications for the entire family. The fear and uncertainty that accompany cancer recurrence can lead to anxiety, stress, and even depression among siblings and parents alike. Understanding these emotional aspects is essential for healthcare providers as they develop comprehensive care plans that trumpet the importance of mental and emotional well-being alongside physical health.
Providing appropriate psychological support can help address these issues, ultimately allowing families to cope better with the challenges posed by ongoing surveillance and potential recurrences. Engaging multidisciplinary teams that include psychologists, social workers, and support groups can create a more robust support system for families affected by pediatric gliomas. This holistic approach to care acknowledges that treatment extends beyond the clinic and addresses the interconnectedness of mental and emotional health within the broader framework of childhood cancer.
Utilizing Institutional Partnerships for Comprehensive Cancer Research
Collaborative research efforts among institutions like Mass General Brigham, Boston Children’s Hospital, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute exemplify the power of partnerships in advancing pediatric cancer research. By pooling resources and expertise, these institutions can conduct large-scale studies that yield valuable data, ultimately benefiting patient care. This cooperative framework fosters innovation in the field of pediatric gliomas, facilitating the development of cutting-edge tools like AI for predicting cancer recurrence.
These partnerships are pivotal in establishing best practices and formulating evidence-based protocols that improve outcomes for children battling brain cancer. The focus on collaboration underscores the necessity of teamwork in overcoming the complexities associated with childhood cancers, as it brings together diverse skill sets to tackle pressing questions that impact treatment and recovery. By championing cooperative research, we empower the future of childhood cancer care through shared knowledge and experience.
Future Perspectives: Clinical Trials and Their Significance
As researchers make headway in AI predictive modeling and other advanced technologies, the transition to clinical trials marks a significant milestone in validating these innovations for real-world application. Clinical trials not only test the efficacy of new predictive tools but also enable researchers to gather vital feedback from patient outcomes that can refine and enhance methods for monitoring and managing pediatric gliomas. The quest for more accurate methods to anticipate cancer recurrence rests on these trials, which underscore the importance of evidence-based approaches in pediatric oncology.
Moreover, clinical trials pave the way for the adoption of personalized medicine strategies, wherein treatments are tailored to individual risk profiles based on nuanced predictive analytics. The insights gained from these trials can inform the standard of care, leading to more targeted interventions and ultimately improving survival rates among children with brain cancers. Engaging families in the trial process, ensuring they are well-informed and supportive, will be crucial as we strive towards innovative solutions that can transform the landscape of childhood cancer care.
How to Support Families Affected by Pediatric Cancer
Supporting families dealing with brain cancer in children requires compassion and understanding. Providing resources such as counseling, education about the disease, and connections to community support groups can play a significant role in alleviating the burden on affected families. Equipping caregivers with the tools they need will foster a sense of empowerment, allowing them to navigate the complexities of treatment, relapse risks, and emotional challenges.
Moreover, encouraging open communication between healthcare providers and families is vital to ensure that families feel heard and supported throughout their journey. Regular updates, educational materials, and emotional support should be part of a comprehensive care plan that acknowledges the unique challenges of pediatric oncology. Building a strong support network will help families tackle the uncertainties surrounding treatment and foster resilience as they manage the ongoing journey of childhood cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are pediatric gliomas and how do they relate to brain cancer in children?
Pediatric gliomas are a type of brain tumor that develops from glial cells in children. These tumors can lead to significant complications, including brain cancer in children. Treatment often involves surgery, and while many cases are curable, there’s a risk of recurrence that requires careful monitoring.
How does AI predictive modeling improve the diagnosis of brain cancer in children?
AI predictive modeling enhances the diagnosis of brain cancer in children by analyzing multiple brain scans over time. This technology focuses on identifying subtle changes that could indicate cancer recurrence, providing a more accurate picture than traditional single-scan methods.
What is the importance of temporal learning in predicting brain cancer recurrence in children?
Temporal learning is crucial in predicting brain cancer recurrence because it allows AI models to analyze a sequence of brain scans taken over time rather than relying on a single image. This approach improves the accuracy of predicting whether pediatric gliomas will recur after treatment.
What advancements have been made in childhood cancer care involving AI technology?
Advancements in childhood cancer care include the development of AI tools that accurately predict the risk of relapse in children with brain cancer. These tools analyze multiple MR scans, offering a promising shift from traditional methods and potentially improving the lives of pediatric glioma patients.
Why is early prediction of cancer recurrence important for children with brain cancer?
Early prediction of cancer recurrence in children with brain cancer is vital as it enables clinicians to tailor follow-up care according to the child’s risk level. It may lead to reduced imaging stress for low-risk patients and proactive treatment for those at higher risk, significantly enhancing childhood cancer care.
What role do age and tumor type play in childhood brain cancer outcomes?
Age and tumor type are significant factors in childhood brain cancer outcomes. Certain pediatric gliomas are more common in specific age groups, and their biological behavior can dictate treatment plans and prognoses, influencing how effectively we can manage brain cancer in children.
What future steps are being considered for AI in managing brain cancer in children?
Future steps involve validating AI predictive models in broader clinical settings and initiating clinical trials to determine if AI-informed predictions can optimize care, possibly reducing unnecessary imaging or facilitating earlier intervention in high-risk pediatric glioma patients.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| AI Tool Introduction | An AI tool has been developed to analyze brain scans more accurately for predicting relapse in pediatric cancer patients. |
| Study Collaboration | The study involved researchers from Mass General Brigham, Boston Children’s Hospital, and Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center. |
| Temporal Learning Technique | Temporal learning utilized to combine findings from multiple scans over time, significantly improving predictive accuracy. |
| Prediction Accuracy | The AI tool predicts cancer recurrence with 75-89% accuracy, much higher than the 50% accuracy from single scans. |
| Clinical Relevance | Potential improvements in patient care, such as reducing stressful imaging frequency for low-risk patients. |
Summary
Brain cancer in children can be distressing for families, but advances in AI technology are promising in improving its management. The development of an AI tool that outperforms traditional methods in predicting relapse risks provides a hopeful outlook for better care. By utilizing temporal learning on multiple brain scans, researchers are able to enhance prediction accuracy and ultimately aim to tailor follow-up treatment strategies for pediatric glioma patients. This could significantly reduce the stress of unnecessary imaging for families, ensuring that children receive the most effective care tailored to their specific needs.