Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked intense debate among nutritionists, researchers, and health enthusiasts alike. While sugar can indeed stir cravings and compel some individuals to seek out sweet treats, it doesn’t fit the strict clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as alcohol or nicotine. Nonetheless, the effects of sugar on health cannot be ignored, especially in an era where processed foods laden with added sugar dominate the food landscape. Understanding sugar addiction and its implications is crucial for those looking to manage their sugar cravings and reduce their sugar intake responsibly.
Exploring the nature of sugar dependency reveals a complex interaction between our bodies and the sweet substance found in many foods. Often referred to as sweet fare, sugar has been linked to a myriad of health concerns due to its prevalence in junk foods and sugary beverages. While we often categorize substances like tobacco and certain drugs as addictive, the nuanced role that sugar plays in our diets prompts us to rethink its classification. The ongoing discussions surrounding sugar cravings and the physical and psychological effects it engenders highlight the need for strategic approaches to moderating our consumption of processed foods. In this light, acknowledging the signs of sugar dependency can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
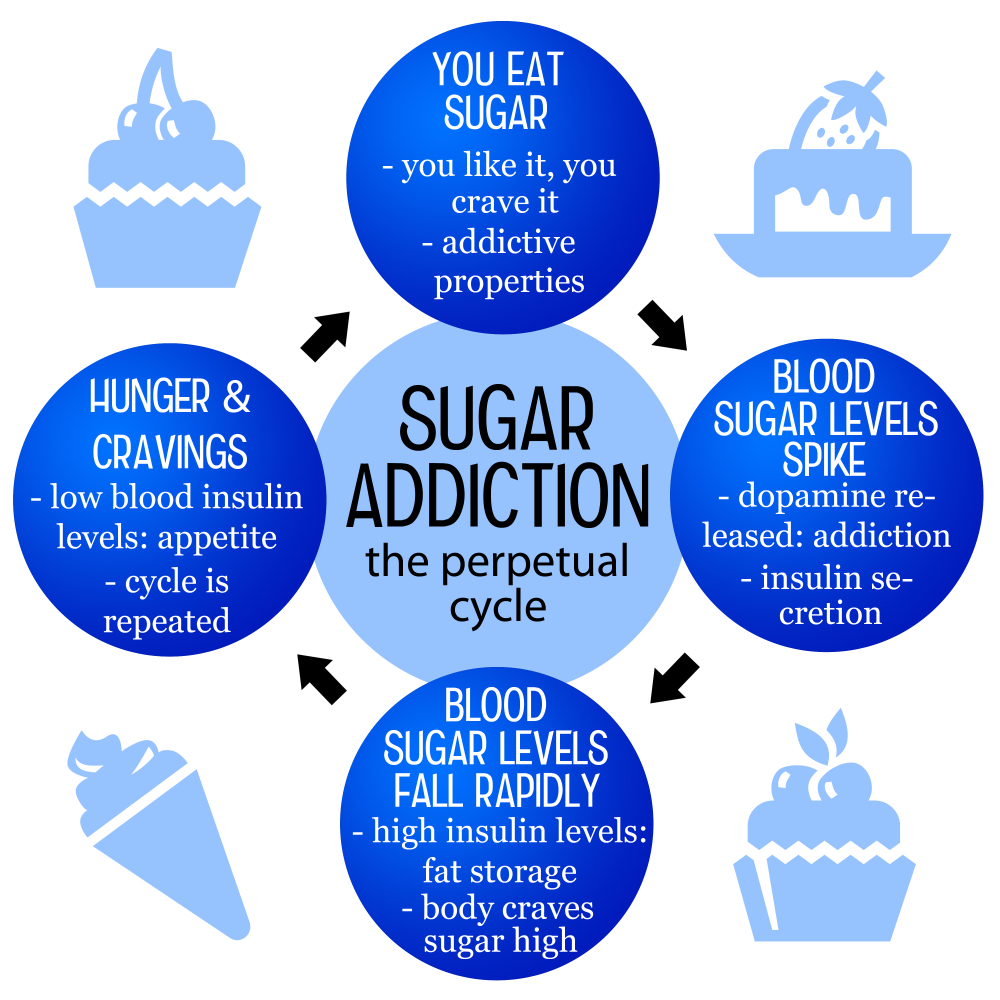
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked significant debate among health professionals. Some experts liken sugar cravings to the compulsive behaviors associated with drugs like nicotine and alcohol. While sugar can trigger similar pathways in the brain that lead to an increase in craving and consumption, it is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical standards. Instead, sugar leads to habitual intake of ultra-processed foods that often contain unhealthy fats and sodium, which can further enhance cravings and undermine nutritional health. This is especially concerning given that the average American consumes almost 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, far exceeding recommended limits.
Withdrawal symptoms can occur when individuals drastically reduce sugar intake, manifesting as headaches, irritability, and anxiety. These symptoms, while uncomfortable, often do not reach the severity seen in the withdrawal from narcotics or alcohol. Therefore, you may experience a ‘sugar detox,’ but it’s essential to approach sugar reduction thoughtfully rather than suddenly eliminating sugar from the diet. Moderation is key, and understanding the distinction between necessary carbohydrates present in nutritious foods versus added sugars in processed products is critical for maintaining balanced dietary habits.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
Excessive sugar consumption has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and even certain types of cancer. The body’s response to high sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, which is a precursor to many of these serious conditions. Moreover, the palatability of sugar-laden foods makes these items often difficult to resist, perpetuating a cycle of unhealthy eating behaviors. A diet high in processed sugars can disrupt metabolic health, impacting overall energy levels and leading to chronic fatigue.
Additionally, sugar can significantly affect mental health. Studies have suggested that high sugar intake is associated with an increased risk of mood disorders, including depression and anxiety. Sugar cravings can induce symptoms akin to addiction, where individuals may consume sugary foods for emotional comfort. Therefore, reducing sugar intake can not only benefit physical health but also improve mental well-being. A balanced approach to sugar, focusing on intrinsic sugars found in whole foods like fruits and vegetables, can lead to better health outcomes.
Incorporating healthier alternatives and gradually reducing added sugars can significantly impact overall health and wellness. Regularly reviewing nutritional labels and being mindful of hidden sugars in processed foods can empower individuals to make more informed dietary choices.
Addressing Sugar Cravings
Sugar cravings are a common challenge faced by many individuals seeking to improve their diets. These cravings can stem from various sources, including emotional eating, habitual patterns, or the brain’s reward system seeking quick energy bursts. The prevalence of highly palatable processed foods makes it easy to reach for sugary snacks when hunger strikes, often leading to overconsumption and a cycle of cravings. Understanding the nature of sugar cravings is essential for developing strategies to overcome them.
To address sugar cravings effectively, individuals may benefit from incorporating whole, nutrient-dense foods into their diets that provide sustained energy without excessive sugar. High-fiber foods, such as legumes, whole grains, and vegetables, can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the desire for sugary snacks. Additionally, practicing mindful eating can foster awareness of hunger signals and emotions associated with cravings, allowing for healthier coping mechanisms. Gradually replacing sugary snacks with healthier options can diminish the allure of sugar over time.
Processed Foods and Sugar Intake
The modern food landscape is riddled with processed foods that contain added sugars, making it increasingly difficult for individuals to manage their sugar intake. These foods often provide little nutritional value but are engineered to be hyper-palatable, leading to overconsumption and contributing to health problems such as obesity and metabolic syndrome. It’s crucial for consumers to understand how processed foods can perpetuate sugar dependency and cravings.
Educating oneself on recognizing processed foods and their sugar content can empower individuals to make healthier choices. Opting for whole foods over processed versions is a fundamental step toward reducing sugar intake. Cooking from scratch, using fresh ingredients, and reading labels to understand added sugars can create a more balanced diet. The shift toward more whole foods can not only minimize sugar consumption but also enhance overall nutritional quality.
Reducing Sugar Intake: Practical Steps
Reducing sugar intake can seem daunting, especially given its ubiquity in modern diets. However, adopting a gradual approach can yield sustainable results. Begin by tracking daily sugar consumption and identifying sources of added sugars, such as sugary beverages, snacks, and desserts. From there, individuals can set realistic goals for sugar reduction, such as limiting added sugars to recommended levels set by health organizations.
Practical steps include replacing sugary drinks with water or herbal teas, choosing fresh fruits over candy or processed desserts, and preparing meals at home to control ingredients. Moreover, experimenting with natural sweeteners like stevia or honey can satisfy sweet cravings without the adverse effects of traditional sugars. Over time, these incremental dietary changes can lead to reduced cravings and a healthier relationship with sugar.
The Importance of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating plays a critical role in managing sugar consumption and cravings. By being present during meals and snacks, individuals can better assess their hunger levels and make conscious choices about what they consume. This practice encourages a greater appreciation for food and can reduce mindless snacking, particularly on sugary options that may offer only temporary satisfaction.
Incorporating mindfulness into eating habits can involve simple techniques such as slowing down during meals, savoring each bite, and listening to the body’s hunger cues. Keeping a food diary can also help individuals reflect on their eating habits and identify patterns related to sugar cravings. Mindful eating not only helps regulate sugar intake but also fosters a more positive attitude toward healthy eating, allowing individuals to enjoy their food while maintaining their health.
Sugar and Emotional Well-Being
The connection between sugar intake and emotional well-being is an area of growing research. Many people turn to sugary foods as comfort during stress or sadness, creating a link between emotions and sugar consumption. While sugar can provide a temporary boost in mood, the aftermath often results in a crash that can exacerbate feelings of anxiety or depression.
To break the cycle of emotional eating, it is essential to explore alternative coping strategies that do not involve sugar. Engaging in physical activity, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga, and seeking social support can serve as healthier outlets for managing emotional stress. By building resilience and reducing reliance on sugar for emotional comfort, individuals can enhance their overall mental health and well-being.
Creating a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health and managing sugar intake effectively. By focusing on whole, minimally processed foods, individuals can meet their nutritional needs while reducing excess sugar consumption. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can create a nutrient-dense foundation that supports overall wellness.
Additionally, it’s vital to remember that moderation is key. Instead of completely eliminating sugar, individuals should strive to enjoy moderate amounts, particularly from natural sources like fruits. Building a balanced approach encourages a sustainable lifestyle where occasional indulgence is welcomed without falling into the trap of excessive sugar consumption. Educating oneself about nutritional choices can significantly enhance health outcomes in the long run.
The Role of Community in Reducing Sugar Intake
Community support plays a vital role in helping individuals reduce their sugar intake and make healthier choices. Engaging with local organizations or groups focused on nutrition can provide resources, education, and motivation for individuals seeking to cut down on sugar consumption. Community events that promote healthy eating often encourage shared experiences, making it easier to adopt lifestyle changes.
Moreover, communal preparation of meals and sharing recipes can foster a sense of belonging while promoting healthier eating habits. Online platforms and social media also offer opportunities for connecting with like-minded individuals, sharing successes, and exchanging tips on reducing added sugars. Building a supportive community can significantly enhance motivation and accountability for anyone looking to improve their dietary habits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar has some addictive qualities, but the withdrawal symptoms are much milder, making it less severe than substances classified as addictive.
What are the effects of sugar on health?
Excessive sugar intake, particularly from processed foods, can lead to obesity, diabetes, and other chronic health issues. On average, people consume significantly more added sugar than recommended, which can trigger health issues and cravings. Reducing sugar intake gradually can help mitigate these effects.
What causes sugar cravings and how can I manage them?
Sugar cravings are often caused by the consumption of ultra-processed foods that are high in sugar, fat, and sodium. To manage sugar cravings, it’s effective to gradually reduce sugar intake, read food labels, and choose more whole foods instead of sugary snacks.
Are processed foods responsible for sugar addiction?
Processed foods contribute to sugar cravings due to their high palatability and accessibility, often containing added sugars and unhealthy fats. Limiting these foods can help reduce sugar dependence and cravings.
How can I reduce sugar intake effectively?
To effectively reduce sugar intake, check food labels to be aware of added sugars, gradually decrease consumption instead of going cold turkey, and opt for healthier alternatives. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 6 teaspoons for women and 9 teaspoons for men.
Can eliminating sugar from my diet lead to withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, if you suddenly eliminate sugar, especially from processed foods, you may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, or dizziness. It’s often recommended to reduce sugar intake gradually to minimize these effects.
Is sugar addiction real or a myth?
The concept of sugar addiction is debated; while sugar may lead to increased cravings and compulsive eating, it doesn’t fit the strict clinical definition of addiction compared to substances like alcohol or nicotine.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Addiction Classification | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | Though not classified as addictive, sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | These foods, high in sugar, fats, and sodium, increase cravings and the likelihood of habitual consumption. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugary foods can result in symptoms similar to withdrawal, but less severe than those from addictive drugs. |
| Need for Sugar | Sugar is a part of many healthy foods; thus, it is not entirely avoidable like drugs or alcohol. |
| Consumption Recommendations | American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. |
| Healthy Management | Gradually reducing sugar intake is advised rather than a sudden elimination. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This is a thought-provoking question that arises in discussions surrounding dietary habits and health. While sugar may not be classified as an addictive substance by clinical definitions, the patterns of cravings and consumption associated with it suggest that there are strong psychological and physiological influences at play. The prevalence of ultra-processed foods rich in sugar further complicates our relationship with this sweetener. It is crucial to approach sugar consumption mindfully, aware of its presence in various healthy foods, while also recognizing the recommendations for limiting added sugars in our diets. Ultimately, understanding whether sugar is addictive involves a nuanced perspective that balances enjoyment with mindful consumption.